Selected Projects
Doctoral Research
Fall 2024-Present
When high-fidelity data is expensive to obtain in large quantities, engineers often use cheaper “low-fidelity” models instead. Multi-fidelity surrogate modeling combines high and low-fidelity data to train a surrogate model which is cheaper to evaluate than the high-fidelity model, but more accurate than the low-fidelity models. Many existing multi-fidelity approaches rely on Kriging (Gaussian Processes), a nonlinear regression method with built-in uncertainty estimation. These Kriging-based approaches can be classified as either coKriging or autoregressive. CoKriging estimators use multi-output Gaussian Processes to relate the levels of fidelity. This approach is often limited by large matrix inversions and inexpressive kernels. Autoregressive estimators are cheaper to train than coKriging models, but approximate each fidelity-level sequentially using the level immediately beneath it. This induces a Markovian property which ignores statistical information provided by the lower-fidelity functions. Further, autoregressive methods assume a known accuracy hierarchy and some methods assume noiseless or training data. We propose a novel multi-fidelity Kriging method which benefits from the efficiency of autoregressive estimators while removing the limiting Markovian structure, accuracy ordering, noiseless/nested training data, and expensive low-fidelity Kriging models. We demonstrate improved accuracy and tighter confidence intervals compared to existing methods on various multi-fidelity test problems.
Georgia Tech MSA Project Week sponsored by Best Buy
Spring 2024

Leveraged techniques in data mining, dimensionality reduction, parallel computing, and visualization to develop a deep learning model that accurately categorized over 500,000 customer service transcripts.
Georgia Tech Modeling & Simulation Term Project
Fall 2023
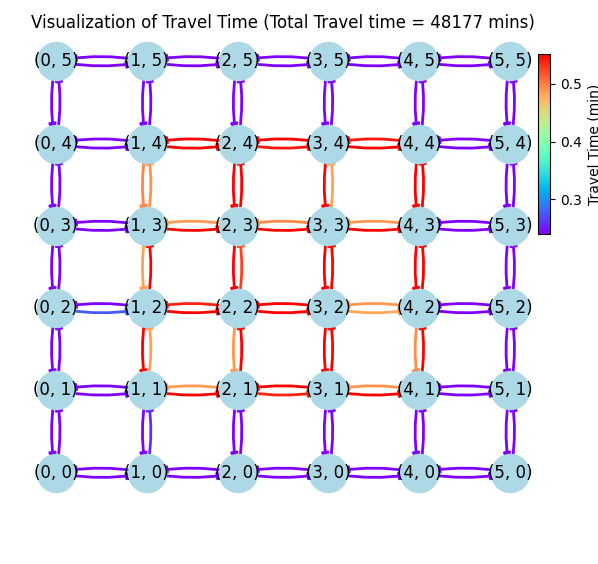
In contemporary transportation systems, the management of traffic flow under heavy load and unpredictable events such as flash floods are a critical challenge. The conventional static traffic assignment, where routes are fixed at the onset, is insufficient in addressing real-time variations in trip volumes, accidents, work zones, and weather conditions. Dynamic Traffic Assignment (DTA) is a pragmatic solution, adapting routing strategies continuously to evolving traffic conditions. Existing navigation services, while adept at adapting to incidents like accidents and road closures, often neglect unreported events like flash floods, posing a significant threat to both drivers and system integrity. By simplifying the traffic network setting, we will replicate diverse flooding intensities, enabling comprehensive evaluation of our dynamic traffic assignment strategy. By systematically analyzing these simulations, our research aims to establish a robust and adaptive framework for rerouting under flash flood conditions, thereby enhancing the resilience and safety of modern transportation networks.
Georgia Tech Data Science for Epidemiology Term Project
Fall 2023
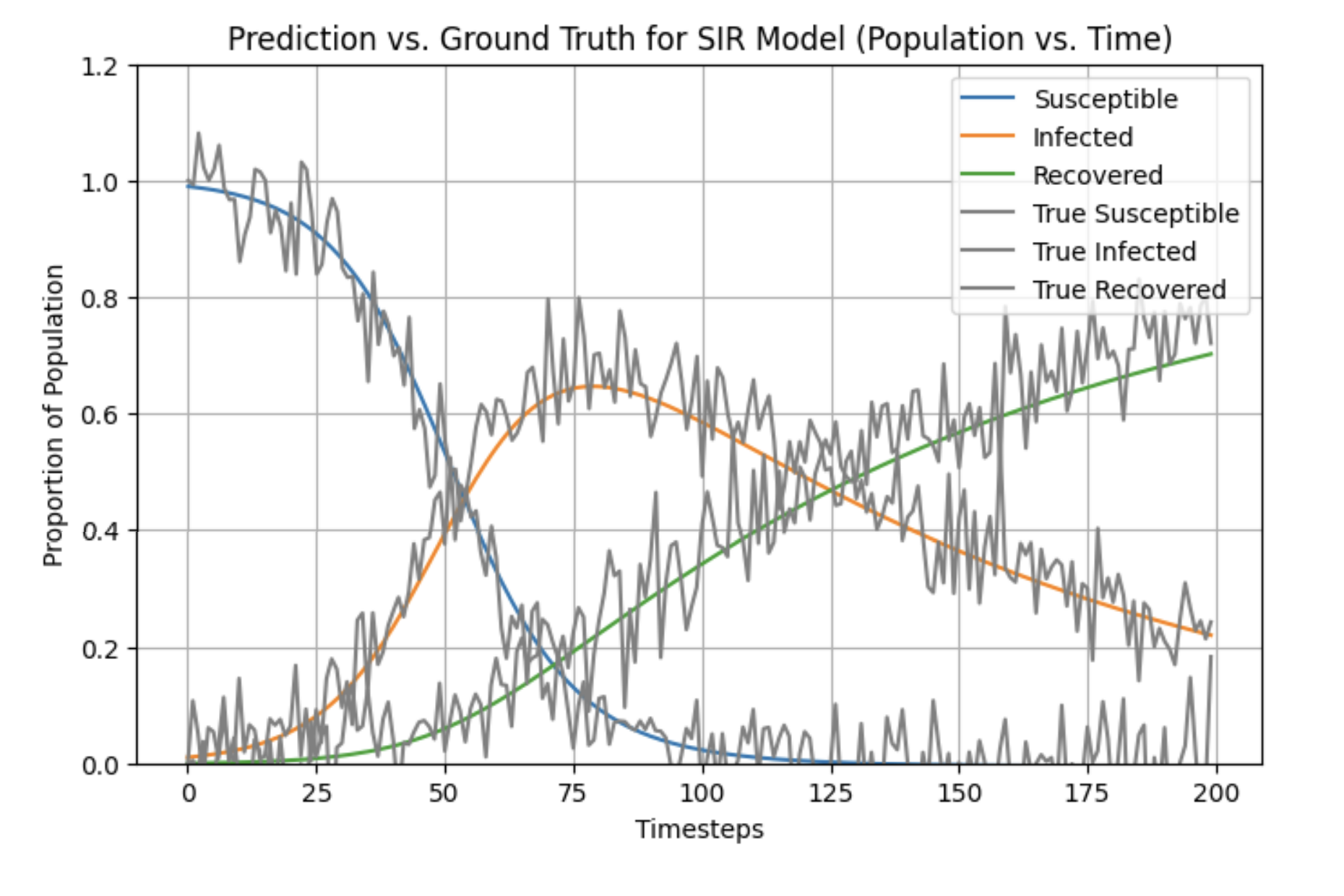
This project outlines how to discover governing differential equations directly from data to determine the overall course of an epidemic. The two methodologies used to accomplish this will be the popular SINDy algorithm, developed by Brunton and Kutz et al. as well as the symbolic regression model applied to the derivative of the model. The group successfully used both methods to recover the SIR model from synthetic data with noise artificially added and to predict COVID-19 data. The PySR model, when effectively regularized showed promise in being able to robustly recover governing differential equations in the presence of noisy data.
Georgia Tech Computational Data Analytics Term Project
Fall 2023
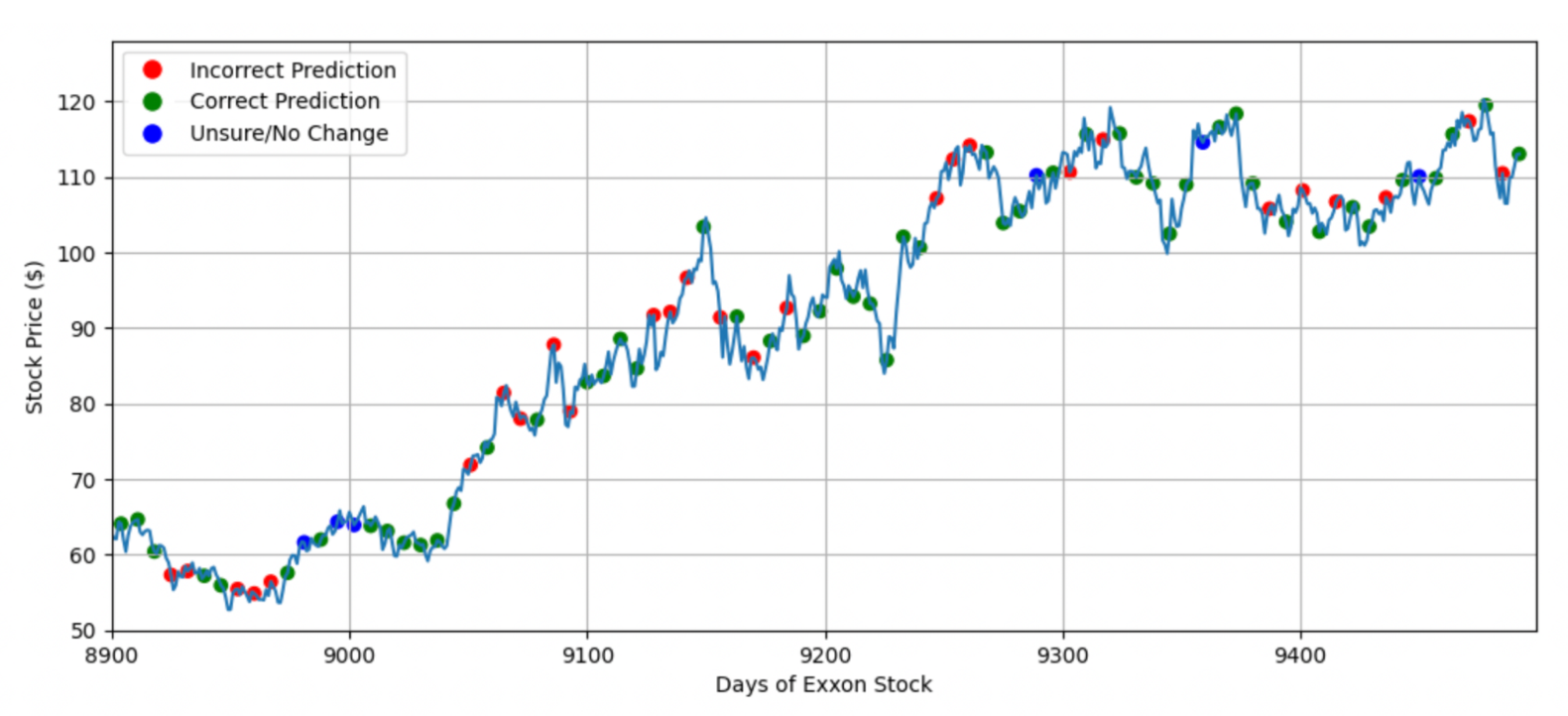
This paper investigates Adaptive Boosting (AdaBoost), Kernel Ridge Regression, and Kernel Support Vector Machines and their ability to predict valuation changes in Exon Mobil stock augmented with exogenous regressors of oil price per barrel, S&P 500 data, google search data, and electric car demand. Further, this report also investigates applying the AdaBoost algorithm to high-frequency trading, optimized and diversified by applying Markowitz Portfolio theory to form a convex minimization problem. The report found that AdaBoost outperformed KRR, and KSVM, especially when the number of rounds of boosting was increased. Further, the portfolio optimization algorithm converged on six companies to apply the algorithm to and outputted the optimal allocation of capital to each strategy. This has strong implications in the field of quantitative finance and was demonstrated to be profitable in this paper.
Virginia Tech Undergraduate Research Project
Fall 2022 - Spring 2023
Advisor: Serkan Gugercin, Ph.D.
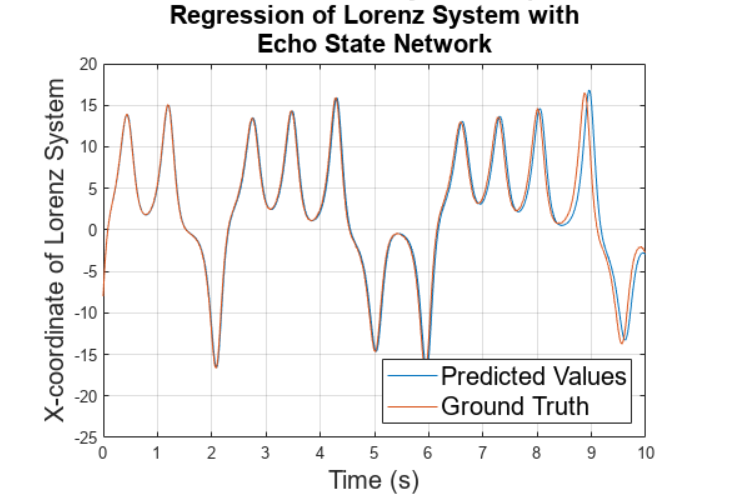
This paper develops a framework for improving upon traditional regression methods to model discrete nonlinear dynamical systems. This framework is derived from a branch of recurrent neural-networks called Echo State Networks (ESNs). This report compares this methodology to the famous Sparse Identification of Nonlinear Dynamics (SINDy) framework developed by Brunton et al. This investigation specifically analyzes the Lorenz System as an example nonlinear and chaotic system. In the models investigated within this report, the Linear ESN model outperforms the SINDy algorithm when noise in the system is sufficiently low. The SINDy algorithm is also far more computationally intensive, requiring much more data to yield comparable results. In addition, SINDy requires sampling of a numerical derivative of a signal. Using finite difference methods amplifies any noise present in the signal, and thus, a direct, discrete method for calculating a regularized derivative is proposed, based on the Total Variation Regularized Derivative (TVD).
Virginia Tech Mechanical Engineering Senior Design Project
Fall 2022 - Spring 2023
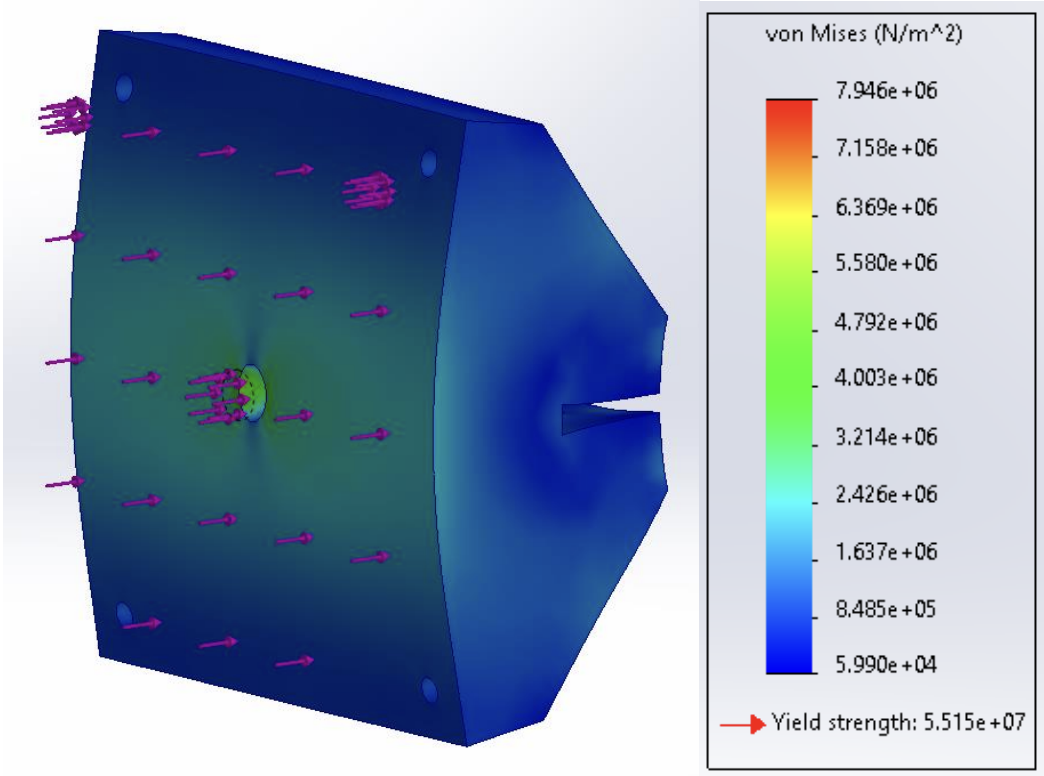
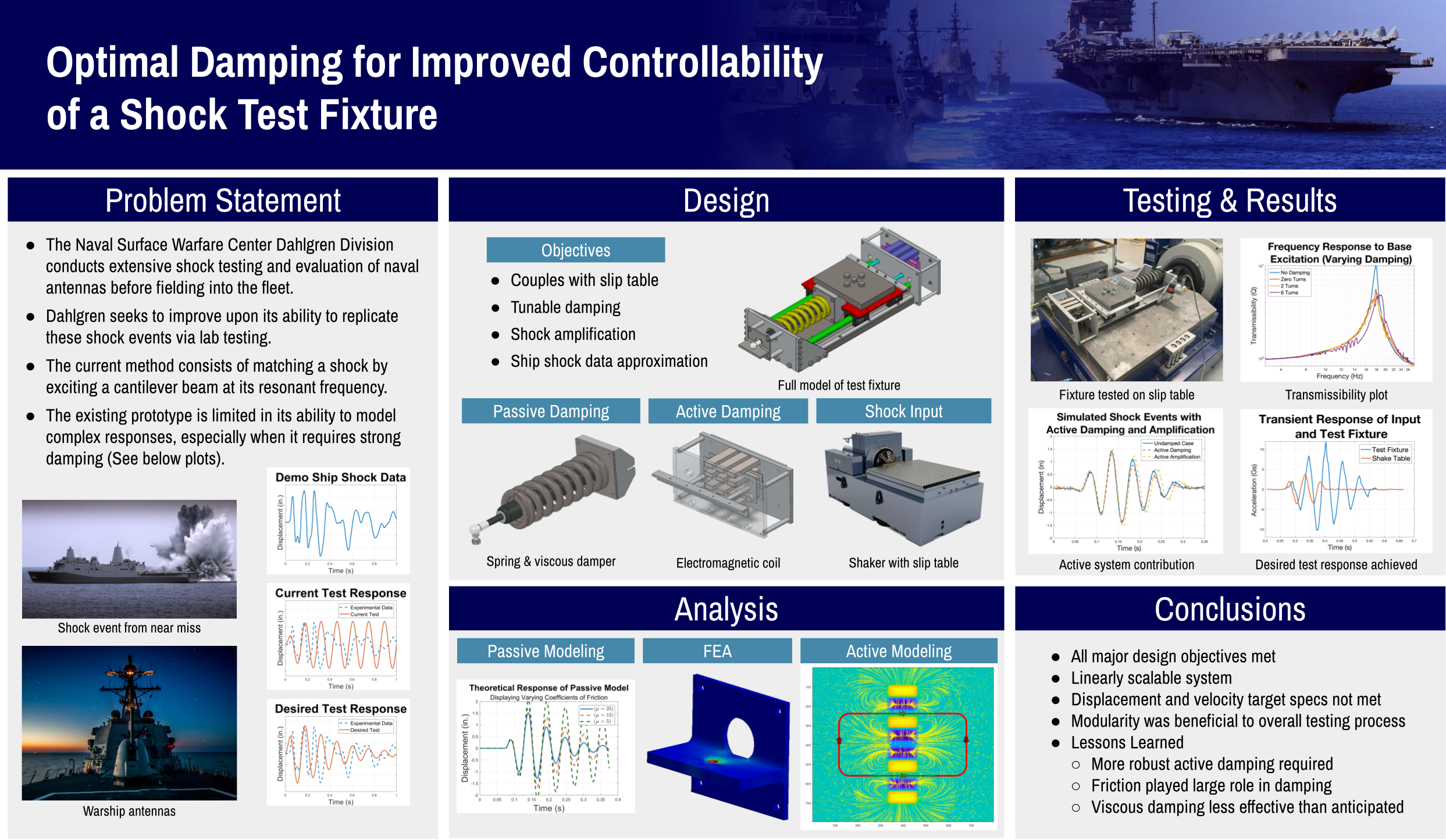
Naval antennas require extensive shock testing and evaluation before being deployed on surface warships. The purpose of this project was to design, simulate, validate, manufacture, and test a prototype that emulates shock impacts on naval communication antennas for the Naval Surface Warfare Center - Dahlgren Division (Dahlgren). The team produced an active and a passive solution with priority on modeling sample shock, which is irregular, high-frequency and high-velocity. The full report covers customer needs, concept generation, prototyping, concept down selection, designs, simulation, analysis, and general team attributes.
Virginia Tech Computational Modeling & Data Analytics Senior Capstone
Spring 2024
Advised by Dr. Mark Embree, this project sought to design a hands-on experiment for students in CMDA 3605 courses to see eigenvalues in action. The experiment involved collecting high-speed video of a swinging pendulum with multiple connected masses, converting the video to time series data, processing the time series data to extract the fundamental frequencies, and finally comparing the experimental values to theoretical ones.